In today’s globalized business landscape, verifying the authenticity of cross-border documents is critical. For international stakeholders dealing with Chinese entities, the Hague Apostille Convention has long been a cornerstone for simplifying document legalization. But as technology reshapes legal processes, China’s 2025 leap into remote video notarization (e-notarization) is transforming how foreign businesses access Apostille services. Let’s explore this shift, its implications, and why it matters for your cross-border operations.
1. The Hague Apostille: A Quick Refresher
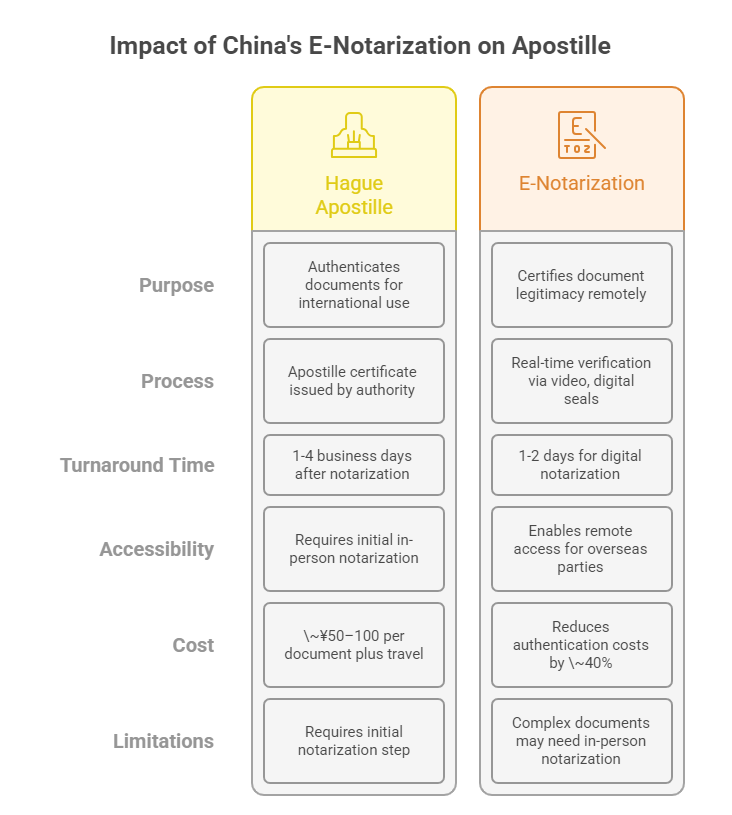
The Hague Convention Abolishing the Requirement for Legalization for Foreign Public Documents (1961) streamlines document authentication across 125+ member countries. Instead of lengthy embassy legalization, an Apostille certificate issued by a designated authority (like China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs or its provincial offices) validates documents for international use. Common documents include:
- Corporate reports (e.g., business licenses, credit filings).
- Legal contracts.
- Educational diplomas.
- Personal affidavits.
In China, Apostille issuance typically takes 1–4 business days, costing ~¥50–100 per document. Yet, the initial notarization step—where a Chinese notary public certifies the document’s legitimacy—historically required in-person visits, creating hurdles for overseas clients.
2. Enter E-Notarization: China’s Digital Revolution
In 2023, China amended its Notarization Law to formalize remote video notarization, accelerating adoption by 2025. This allows:
- Real-time verification: Parties outside China can appear before notaries via secure video platforms.
- Digital seals: E-signatures and blockchain-backed stamps replace physical seals.
- Eligible documents: Corporate filings (e.g., Articles of Incorporation), powers of attorney, and declarations.
How it works:
- Application: Submit documents digitally to a Chinese notary office.
- Video session: Verify identity and intent via encrypted call.
- E-certificate: Receive a digitally notarized document in 24–48 hours.
Example: A U.S. investor needing a notarized Chinese supplier contract can now skip flights to Shanghai—saving weeks and ~$2,000 in travel costs.
3. Synergy with Apostille: Efficiency Gains and Caveats
E-notarization doesn’t replace Apostille but optimizes its workflow:
A. Faster Apostille Turnaround
- Traditional path: Notarization (5–7 days) → Apostille (1–4 days).
- E-notarization path: Digital notarization (1–2 days) → Apostille (1–4 days).
Result: Documents reach Hague member countries 30–50% faster.
B. Broader Accessibility
- Remote sessions enable SMEs, freelancers, and overseas legal teams to access Chinese notary services.
- Non-Hague countries (e.g., UAE, Vietnam) still require consular legalization, but e-notarization simplifies the first step.
C. Limitations to Note
- Complex documents: Property deeds or court rulings may still require in-person notarization.
- Tech barriers: Stable internet and ID verification tools (e.g., facial recognition) are essential.
- Regional compliance: Some Chinese provinces (e.g., Guangdong, Shanghai) lead in e-notarization infrastructure; others lag.
4. Global Implications: Why This Matters in 2025
- Cost reduction: E-notarization cuts authentication costs by ~40% for foreign entities (World Bank, 2024).
- Fraud prevention: Blockchain integration reduces document tampering risks.
- Supply chain agility: Manufacturers can swiftly notarize compliance docs (e.g., ISO certifications) for overseas tenders.
For businesses in non-Hague countries (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Algeria), pairing e-notarization with traditional legalization ensures smoother market entry.
5. The Road Ahead
China aims to integrate e-notarization with its National Online Government Services Platform by 2026, enabling single-portal submissions for notarization and Apostille. Meanwhile, expect:
- AI-assisted verification: Automated checks for document consistency.
- Cross-border reciprocity: Negotiations for mutual e-notarization recognition with the EU and ASEAN.
Conclusion
China’s e-notarization revolution isn’t just about convenience—it’s a strategic upgrade to its global business infrastructure. For overseas partners, this means faster, cheaper, and more secure document authentication, reinforcing China’s commitment to frictionless trade.
As Hague Apostille remains indispensable for international document flows, combining it with e-notarization positions forward-thinking businesses to thrive in cross-border ventures. Stay ahead by leveraging these innovations—your next deal might only be a click away.
Need Apostille services for Chinese documents? Explore our streamlined solutions for Hague Apostille certification, designed for global compliance.
ChinaBizInsight
Your strategic bridge to transparent business in China.

