In international business, trust begins with verified documentation. Yet as cross-border transactions with Chinese entities surge, so do sophisticated document fraud schemes. A single forged certificate can derail partnerships, trigger legal liabilities, and cause six-figure losses.
China processed over 1.2 million Hague Apostilles in 2024 alone – a prime target for counterfeiters. Learn to identify these critical red flags before your next deal:
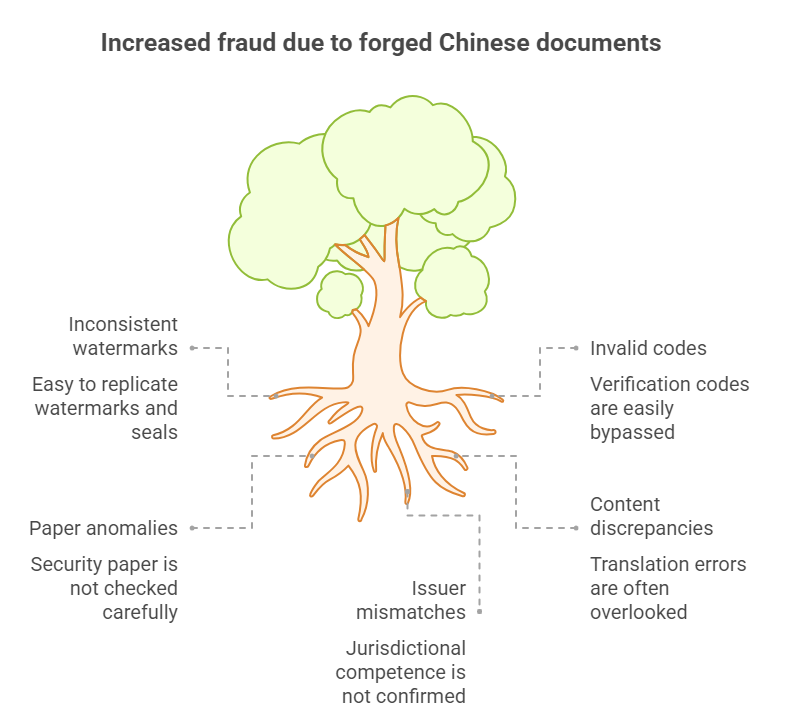
1. Inconsistent Official Watermarks & Seals
Genuine Chinese documents feature multi-layered security:
- Micro-text Patterns: Legitimate Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) watermarks display “中华人民共和国外交部” in repeating micro-font visible under UV light. Counterfeits often show blurred or pixelated text.
- Embossed Holograms: Apostilles contain state emblem holograms that shift color when tilted. Forgeries use static stickers.
- Precision Seal Alignment: Government seals (公章) must perfectly align with registration numbers. Even 1mm deviation indicates tampering.
Case Study: A European importer lost €240,000 after accepting falsified ISO certificates with misaligned Shanghai Notary Office seals.
2. Invalid Verification Codes & QR Links
All Chinese Apostilles since 2023 include digital verification:
- 17-Digit Apostille Number: Cross-check at China’s Official Verification Portal
- Dynamic QR Codes: Authentic codes link directly to government databases (e.g., consular.mfa.gov.cn domains). Hover over links to detect spoofed URLs.
- Real-Time Authentication: Valid documents return issuer details, timestamps, and verification records. “Page not found” errors signal fakes.
Pro Tip: Verify before signing contracts – 68% of forgeries are detected through portal checks (MFA 2025 data).
3. Paper Quality & Printing Anomalies
China uses exclusive security paper:
- Invisible Fibers: Genuine documents show blue/red threads under magnification.
- Anti-Copy Patterns: “VOID” patterns emerge when scanned or photocopied.
- Raised Inks: Official seals use thermochromic ink that disappears briefly under heat friction.
Red Flag Alert: Smudged ink, perforation mismatches, or incorrect paper weight (standard = 80gsm) indicate forgeries.
4. Content Discrepancies & Translation Errors
Scrutinize linguistic and formatting details:
- Mandatory Elements: Apostilles require 10 standardized fields including issuer’s name, capacity, and seal.
- Consistent Translations: Company names must match National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System records.
- Formatting Rules: Apostille numbers follow YYYY-XX-XXXXXX format. Deviations like “AP-2025-123” are invalid.
Example: A forged Guangdong business license listed “注册资本 (Registered Capital)” as “RMB 5,000,000” instead of “人民币伍佰万元” – a fatal syntax error.
5. Issuer Authority Mismatches
Confirm jurisdictional competence:
- Provincial Limitations: Local Foreign Affairs Offices (FAOs) can only notarize documents from their administrative region.
- Apostille Issuers: Only MFA and 31 delegated provincial FAOs hold authority.
- Common Forgery Tactics: Fake “Beijing FAO” stamps on Shanghai documents, or forged MFA seals for provincial-level papers.
Protect Your Business: Verification Protocol
- Digital Authentication: Immediately verify QR codes/certificate numbers at China’s verification portal
- Source Validation: Request original document tracking numbers from providers
- Professional Verification: For high-value transactions, engage third-party validators like ChinaBizInsight’s Document Verification Service
International trade thrives on trust – but trust requires verification. As document forgery techniques evolve, combining technological checks with human expertise remains your strongest defense.
ChinaBizInsight
Your strategic bridge to transparent business in China.

